Imagine you're in a bustling marketplace. Vendors are shouting out their wares, and customers are haggling over prices. Now, picture two different systems for keeping track of all these transactions. One is a centralized ledger, managed by a single authority, and the other is a decentralized ledger, where everyone in the market has a copy of the ledger and can verify transactions. Which would you trust more? This is the essence of the debate between blockchain and traditional databases. So, let's dive in and explore blockchain vs database, and see which one might be the better fit for your needs.
Understanding the Basics
What is a Database?
A database is a structured collection of data stored electronically. Think of it like a digital filing cabinet where information is organized in tables, rows, and columns. Traditional databases are managed by a central authority, which controls access and ensures data integrity. They are widely used in various applications, from customer relationship management (CRM) systems to e-commerce platforms.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain, on the other hand, is a type of distributed system that uses a decentralized ledger to record transactions. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, and once a block is added, it becomes part of a permanent and immutable record that cannot be altered retroactively. This makes blockchain highly secure and transparent. It's like a public ledger that everyone can see but no one can tamper with.
Key Differences
Decentralization vs Centralization
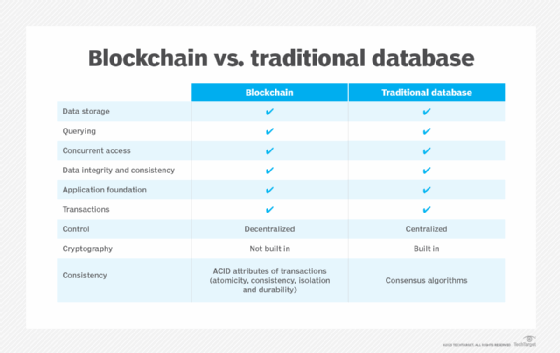
One of the most significant differences between blockchain and databases is their approach to data management. Traditional databases are centralized, meaning a single entity controls the data. This can be efficient but also poses risks, such as single points of failure and potential data breaches. In contrast, blockchain operates on a decentralized model, where data is distributed across multiple nodes. This decentralized ledger ensures that no single entity has control over the data, making it more resilient and secure.
Data Storage and Access
In a traditional database, data storage is straightforward. Data is stored in a structured format, making it easy to retrieve and manipulate. However, this also means that the data can be easily altered or deleted. Blockchain, however, uses a different approach. Data is stored in blocks that are linked together in a chain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, ensuring that any attempt to alter the data would be immediately detectable. This makes blockchain an excellent choice for applications that require immutable records.
Security and Cryptography
Security is a critical aspect of both blockchain and databases, but they achieve it in different ways. Traditional databases rely on firewalls, encryption, and access controls to protect data. While these measures are effective, they are not foolproof. Blockchain, however, uses advanced cryptography to secure data. Each transaction is verified by multiple nodes in the network, and once verified, it is added to the blockchain. This makes blockchain highly resistant to hacking and fraud.
Use Cases
When to Use a Database
Traditional databases are ideal for applications that require fast data retrieval and manipulation. For example, e-commerce platforms, CRM systems, and content management systems (CMS) all benefit from the structured and centralized nature of databases. If you need to quickly update customer information or process transactions, a database is likely the better choice.
When to Use Blockchain
Blockchain, on the other hand, is perfect for applications that require high levels of security and transparency. For instance, supply chain management, voting systems, and financial transactions can all benefit from the immutable records and decentralized nature of blockchain. If you need to ensure that data cannot be tampered with and that all parties have access to the same information, blockchain is the way to go.
Conclusion
So, which is better: blockchain or database? The answer depends on your specific needs. If you require fast data retrieval and manipulation, a traditional database might be the better choice. However, if security, transparency, and decentralization are your top priorities, blockchain could be the way forward. Both technologies have their strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these can help you make an informed decision.
As you navigate the world of data management, remember that the choice between blockchain and database is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It's about finding the right tool for the job. So, take the time to assess your needs, weigh the pros and cons, and make a decision that aligns with your goals.
Now, I'd love to hear from you. Have you used blockchain or databases in your projects? What was your experience like? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between blockchain and a traditional database?
The main difference lies in their architecture. Traditional databases are centralized, managed by a single entity, and allow for easy data manipulation. Blockchain, however, is decentralized, uses a distributed ledger, and ensures data immutability through cryptography.
2. Can blockchain replace traditional databases?
Blockchain and traditional databases serve different purposes. While blockchain offers unique advantages in terms of security and transparency, traditional databases are often more efficient for fast data retrieval and manipulation. They are not direct replacements but can complement each other in various applications.
3. How does blockchain ensure data security?
Blockchain uses advanced cryptography to secure data. Each transaction is verified by multiple nodes in the network, and once verified, it is added to the blockchain. This makes it highly resistant to hacking and fraud.
4. What are some real-world applications of blockchain?
Blockchain is used in various industries, including supply chain management, financial transactions, voting systems, and smart contracts. Its decentralized and immutable nature makes it ideal for applications that require high levels of security and transparency.
5. Can blockchain be used for data storage?
While blockchain can be used for data storage, it is not as efficient as traditional databases for large-scale data storage due to its decentralized and immutable nature. However, it is excellent for storing critical and sensitive data that requires high security and transparency.
```
Posting Komentar