Imagine a world where data is not just stored but is also tamper-proof, transparent, and accessible to all authorized parties. Welcome to the realm of blockchain as a database. This revolutionary technology, initially famous for powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is now transforming how we think about data management. But how exactly can blockchain serve as a database? Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating possibilities.
Understanding Blockchain as a Database
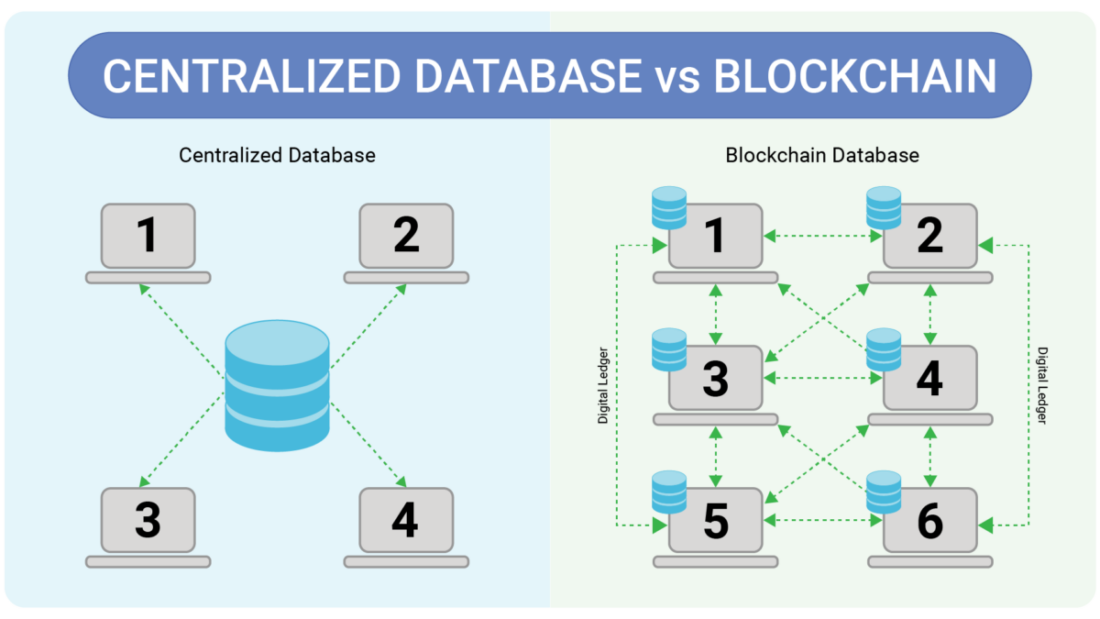
At its core, blockchain is a type of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). Instead of relying on a single central authority to manage and verify data, blockchain distributes this responsibility across a network of nodes. Each node holds a copy of the ledger, ensuring that any changes are validated by consensus. This decentralized approach not only enhances security but also ensures Data Integrity.
The Power of Immutable Records
One of the standout features of blockchain is its ability to create immutable records. Once data is added to a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability is achieved through cryptographic security. Each block in the chain contains a unique cryptographic hash that links it to the previous block. Any attempt to tamper with the data would change the hash, alerting the network to the alteration. Think of it like a digital seal that ensures the authenticity and integrity of the information.
Smart Contracts: Automating Trust
Beyond just storing data, blockchain can also execute smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. Smart contracts automate the process of verifying and enforcing agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency. For example, in a supply chain, smart contracts can automatically trigger payments once goods are delivered, ensuring transparency and trust among all parties involved.
Blockchain vs. Traditional Databases
So, how does blockchain differ from traditional databases? Traditional databases are centralized, meaning a single entity controls the data. This centralization can lead to vulnerabilities, such as data breaches and single points of failure. In contrast, blockchain's decentralized nature makes it inherently more secure. But does this mean blockchain is the perfect solution for all data management needs? Not quite. Let’s explore the pros and cons.
Advantages of Blockchain as a Database
- Enhanced Security: With cryptographic security and decentralization, blockchain offers a robust defense against data breaches.
- Transparency: Every transaction is visible to all participants, ensuring accountability and trust.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, ensuring the integrity of the information.
- Automation: Smart contracts can automate processes, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations
While blockchain has many advantages, it also faces challenges. Scalability is a significant issue. Traditional databases can handle thousands of transactions per second, while blockchain networks like Bitcoin handle only a few. Additionally, the energy consumption of blockchain networks, particularly those using proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, is a growing concern. However, advancements in blockchain technology are addressing these issues, making it more viable for widespread adoption.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain as a Database
Blockchain is not just a theoretical concept; it’s already being used in various industries. For instance, in healthcare, blockchain can securely store patient records, ensuring that only authorized parties can access them. In finance, it can streamline transactions and reduce fraud. Even in supply chain management, blockchain can track the journey of goods from origin to consumer, ensuring transparency and accountability.
For example, IBM's blockchain solutions are being used to enhance supply chain transparency. By providing a tamper-proof record of every transaction, blockchain ensures that all parties can trust the data, reducing the risk of fraud and errors.
The Future of Blockchain as a Database
As we look to the future, the potential of blockchain as a database is immense. With ongoing advancements in technology, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases. But what does this mean for you? Whether you’re a business owner, a developer, or simply someone interested in technology, understanding blockchain’s capabilities can open up new opportunities.
Imagine a world where every transaction, every piece of data, is secure, transparent, and tamper-proof. This is not a distant dream but a reality that blockchain is making possible. By embracing this technology, we can build a more trustworthy and efficient digital ecosystem.
Conclusion
Blockchain as a database offers a revolutionary approach to data management. With its decentralized nature, cryptographic security, and immutable records, it provides a level of trust and transparency that traditional databases cannot match. While there are challenges to overcome, the potential benefits are immense. As we continue to explore and develop this technology, the future of data management looks brighter than ever.
So, are you ready to embrace the future of data management? Whether you’re looking to enhance security, increase transparency, or automate processes, blockchain has something to offer. Dive in, explore the possibilities, and join the revolution. The future of data is here, and it’s blockchain.
FAQs
1. What is the primary advantage of using blockchain as a database?
The primary advantage of using blockchain as a database is its ability to provide Data Integrity and Cryptographic Security. Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered, ensuring the authenticity and trustworthiness of the information.
2. How does blockchain ensure data security?
Blockchain ensures data security through its decentralized nature and cryptographic techniques. Each block in the chain contains a unique cryptographic hash that links it to the previous block. Any attempt to tamper with the data would change the hash, alerting the network to the alteration.
3. Can blockchain be used in traditional industries?
Yes, blockchain can be used in various traditional industries, including healthcare, finance, and supply chain management. Its ability to provide secure, transparent, and tamper-proof records makes it an ideal solution for industries that require high levels of trust and accountability.
4. What are smart contracts, and how do they work?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They automate the process of verifying and enforcing agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency. Smart contracts can be used in various applications, from financial transactions to supply chain management.
5. What are the challenges of using blockchain as a database?
The primary challenges of using blockchain as a database include scalability and energy consumption. Traditional databases can handle thousands of transactions per second, while blockchain networks like Bitcoin handle only a few. Additionally, the energy consumption of blockchain networks, particularly those using proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, is a growing concern.
```
Posting Komentar