 " width="250" height="250">
" width="250" height="250">Imagine you're at a bustling marketplace, where vendors are constantly buying and selling goods. Now, picture a system that records every transaction instantly and securely, ensuring no one can cheat the system. Welcome to the world of blockchain technology, where block time plays a crucial role in maintaining this digital ledger's integrity. But what is block time in blockchain, and why does it matter? Let's dive in and explore the fascinating mechanics of blockchain basics and how block time influences blockchain security and transaction speed.
Understanding Blockchain Basics
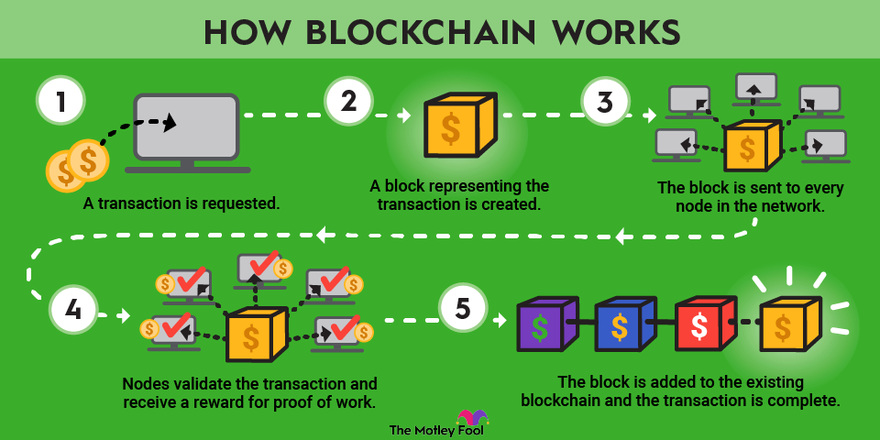
Before we delve into what is block time in blockchain, let's briefly recap blockchain basics. Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, and once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks. This makes blockchain incredibly secure and transparent.
Think of blockchain as a digital notebook that anyone can view but no one can erase or tamper with. Every new entry (or block) is verified by a network of computers before it is added to the chain. This verification process is where block time comes into play.
The Role of Block Time in Blockchain
What is Block Time?
Block time, also known as block interval, is the average time it takes for a new block to be added to the blockchain. It is a critical component of blockchain technology, affecting everything from transaction speed to blockchain security. In simpler terms, block time is the heartbeat of the blockchain, dictating how quickly transactions are confirmed and added to the ledger.
How Does Block Time Work?
To understand what is block time in blockchain, let's use an analogy. Imagine a factory assembly line where each product (block) must pass through several quality checks (verifications) before it can be released. The time it takes for a product to complete this process is analogous to block time. In blockchain, this process involves solving complex mathematical puzzles, known as proof of work, to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain.
Different blockchain networks have different block times. For example, Bitcoin has a block time of approximately 10 minutes, while Ethereum aims for around 12 seconds. These differences are designed to balance security and transaction speed, ensuring that the network remains robust and efficient.
Block Time and Transaction Speed
One of the most significant impacts of block time is on transaction speed. Shorter block times generally mean faster transaction confirmations, which is crucial for applications requiring quick settlements, such as payments and financial transactions. However, there is a trade-off. Shorter block times can potentially compromise blockchain security by making the network more susceptible to attacks, such as 51% attacks, where a malicious actor controls more than half of the network's hashing power.
So, how do blockchain developers strike a balance between transaction speed and security? It often involves a combination of technological innovations and consensus mechanisms. For instance, some blockchains use proof of stake instead of proof of work, which can significantly reduce block times without sacrificing security. Other solutions include layer-2 protocols and sharding, which aim to increase transaction throughput without altering the underlying block time.
Block Time and Blockchain Security
Block time is also a critical factor in blockchain security. Longer block times generally provide more security because they make it harder for attackers to manipulate the blockchain. With longer intervals between blocks, it becomes more difficult for a malicious actor to alter the ledger without being detected. This is why Bitcoin, with its 10-minute block time, is often considered one of the most secure blockchain networks.
However, longer block times can lead to slower transaction confirmations, which may not be ideal for all use cases. This is where the concept of finality comes into play. Finality refers to the point at which a transaction is considered irreversible. In some blockchains, finality is achieved after a certain number of confirmations, regardless of the block time. This ensures that transactions are secure while still allowing for relatively quick confirmations.
The Future of Block Time in Blockchain
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, so too will our understanding and implementation of block time. Developers are constantly exploring new ways to optimize block times to improve transaction speed and security. For example, the transition from proof of work to proof of stake in Ethereum's upcoming upgrades aims to reduce block times and increase scalability.
Moreover, emerging technologies like quantum computing and artificial intelligence could revolutionize how we think about block time and blockchain security. These advancements may enable even faster and more secure transaction processing, making blockchain technology more accessible and efficient for a wider range of applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, what is block time in blockchain is a fundamental question that touches on the very essence of how blockchain technology operates. Block time influences transaction speed, blockchain security, and the overall efficiency of the network. As we continue to explore and innovate in the world of blockchain, understanding and optimizing block time will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of this transformative technology. So, whether you're a seasoned blockchain enthusiast or just dipping your toes into the world of decentralized ledgers, grasping the concept of block time is essential for navigating the exciting and ever-changing landscape of blockchain technology.
FAQs
What is the ideal block time for a blockchain network?
The ideal block time depends on the specific use case and requirements of the blockchain network. For applications requiring fast transaction confirmations, shorter block times are preferable. However, for networks prioritizing security, longer block times may be more suitable. It's all about finding the right balance.
How does block time affect mining?
Block time directly impacts mining by determining how frequently new blocks are added to the blockchain. Shorter block times mean more frequent mining rewards, but they also increase competition among miners. Longer block times reduce competition but may result in fewer mining opportunities.
Can block time be adjusted after a blockchain is launched?
Adjusting block time after a blockchain is launched can be challenging and often requires a hard fork, which involves creating a new version of the blockchain with the desired changes. This process can be complex and contentious, as it requires consensus among network participants.
What are some examples of blockchains with different block times?
Bitcoin has a block time of approximately 10 minutes, while Ethereum aims for around 12 seconds. Other blockchains, like Litecoin, have a block time of about 2.5 minutes. Each blockchain's block time is designed to balance security and transaction speed based on its specific use case.
How does block time relate to consensus mechanisms?
Block time is closely related to consensus mechanisms, which determine how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain. For example, proof of work blockchains like Bitcoin have longer block times to ensure security, while proof of stake blockchains like Ethereum can achieve shorter block times with different validation methods.
```
Posting Komentar