Imagine you're in a bustling marketplace. Vendors are shouting out their prices, and customers are haggling over deals. Now, picture two different ways to keep track of all these transactions: a traditional ledger and a decentralized ledger. The traditional ledger is like a single notebook where one person writes down all the transactions. The decentralized ledger, on the other hand, is like having multiple notebooks, each held by different people, all updating simultaneously. This is the essence of the difference between blockchain and traditional database. Let's dive deeper into this fascinating world of data management.
Understanding Traditional Databases
Traditional databases have been the backbone of data management for decades. They are centralized systems where data is stored in a single location, managed by a database administrator. Think of it as a library where one librarian keeps track of all the books. This centralized approach has its advantages, such as ease of management and quick data retrieval. However, it also comes with significant drawbacks, particularly in terms of blockchain security and data transparency.
Centralized Control
In a traditional database, all the power lies with the administrator. This central authority controls who can access the data, make changes, and ensure its integrity. While this can be efficient, it also creates a single point of failure. If the administrator makes a mistake or is compromised, the entire database is at risk. This lack of decentralization is a major concern in today's digital age, where data breaches and cyber-attacks are all too common.
Data Transparency
Another issue with traditional databases is data transparency. Since the data is controlled by a single entity, there's often a lack of transparency. Users may not know who has access to their data, how it's being used, or if it's being altered without their knowledge. This opacity can lead to mistrust and concerns about privacy and security.
Exploring Blockchain Technology
Blockchain, on the other hand, is a type of distributed ledger technology that operates on a decentralized model. Instead of a single notebook, imagine a network of notebooks, each held by different people, all updating simultaneously. This is the core of blockchain's strength. Let's break down how it works and why it's different from traditional databases.
The Decentralized Ledger
In a blockchain, data is stored across a network of computers, not in a single location. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, and once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks. This makes blockchain incredibly secure and transparent. There's no single point of failure, and any attempt to tamper with the data is immediately noticeable.
Blockchain Security
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain is its blockchain security. Because the data is distributed across a network, it's much harder for hackers to compromise. They would need to attack multiple points simultaneously, which is virtually impossible. This decentralized approach also ensures that the data is always available, even if some nodes go offline.
Data Transparency
Blockchain also excels in data transparency. Every transaction on the blockchain is visible to all participants. This transparency builds trust and ensures that everyone has access to the same information. It's like having a public ledger where everyone can see the transactions, but no one can alter them without consensus.
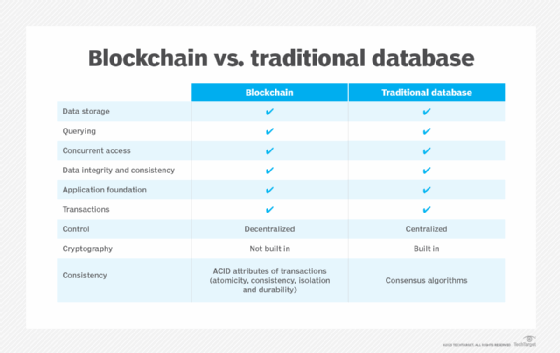
Comparing Blockchain and Traditional Databases
So, what's the real difference between blockchain and traditional database? Let's compare them side by side.
Control and Management
In a traditional database, control is centralized. A single administrator manages the data, which can be efficient but also risky. In contrast, blockchain operates on a decentralized model, where control is distributed across a network. This makes it more secure and resilient but also more complex to manage.
Security
Traditional databases are vulnerable to attacks because they have a single point of failure. Blockchain, with its distributed ledger, is much more secure. Any attempt to tamper with the data is immediately noticeable, making it nearly impossible for hackers to succeed.
Transparency
Traditional databases often lack transparency, with data controlled by a single entity. Blockchain, on the other hand, is transparent by design. Every transaction is visible to all participants, building trust and ensuring data integrity.
Use Cases and Applications
Both blockchain and traditional databases have their unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different use cases. Traditional databases are ideal for applications that require quick data retrieval and centralized control, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. Blockchain, however, is perfect for applications that require high security and transparency, such as financial transactions, supply chain management, and voting systems.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between blockchain and traditional database is crucial in today's digital world. While traditional databases offer ease of management and quick data retrieval, they lack the security and transparency that blockchain provides. Blockchain's decentralized ledger technology ensures that data is secure, transparent, and always available. As we move forward, it's essential to consider the strengths and weaknesses of both systems and choose the one that best fits our needs. So, which one do you think is right for your next project? The choice is yours, but remember, the future of data management is here, and it's decentralized.
FAQs
1. What is the primary difference between blockchain and traditional database?
The primary difference lies in their architecture. Traditional databases are centralized, with data stored in a single location and managed by an administrator. Blockchain, however, is decentralized, with data distributed across a network of computers, ensuring higher security and transparency.
2. How does blockchain ensure data security?
Blockchain ensures data security through its decentralized ledger technology. Data is stored across a network, making it difficult for hackers to compromise. Any attempt to tamper with the data is immediately noticeable, as it would require altering all subsequent blocks in the chain.
3. Can blockchain be used for all types of data management?
While blockchain offers many advantages, it may not be suitable for all types of data management. Traditional databases are often more efficient for applications that require quick data retrieval and centralized control. Blockchain, however, is ideal for applications that require high security and transparency.
4. What are some real-world applications of blockchain?
Blockchain has a wide range of applications, including financial transactions, supply chain management, voting systems, and smart contracts. Its decentralized nature makes it ideal for any application that requires secure and transparent data management.
5. How does data transparency work in blockchain?
In blockchain, every transaction is visible to all participants. This transparency ensures that everyone has access to the same information, building trust and ensuring data integrity. It's like having a public ledger where everyone can see the transactions, but no one can alter them without consensus.
```
Posting Komentar