Imagine a world where transactions are transparent, secure, and tamper-proof. Welcome to the realm of blockchain technology. But have you ever wondered what lies within a single block of this revolutionary blockchain data structure? Let's dive in and explore the intricate components that make up a blockchain block.
The Anatomy of a Blockchain Block
At its core, a blockchain block is a digital container that holds a set of blockchain transactions. Think of it as a digital ledger page, where each page is a block, and the entire book is the blockchain. But what exactly is inside this digital ledger page?
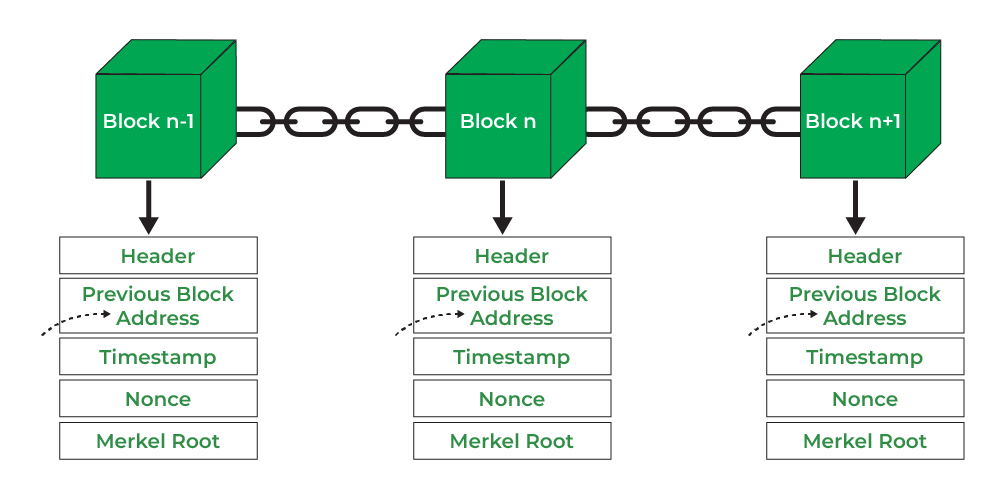
Block Header
The block header is the first part of a blockchain block. It contains crucial metadata that identifies the block and ensures its integrity. The block header includes several key components:
- Version: This indicates the version of the blockchain protocol being used. It ensures that all nodes in the network are on the same page, so to speak.
- Previous Block Hash: This is a unique identifier for the previous block in the chain. It creates a link between blocks, forming an unbreakable chain. If someone tries to alter a block, the hash changes, breaking the chain and alerting the network to the tampering.
- Merkle Root: This is a cryptographic hash that represents all the transactions in the block. It's like a digital fingerprint of the block's contents. Any change in the transactions will alter the Merkle root, ensuring blockchain security.
- Timestamp: This records the exact time when the block was created. It helps in maintaining the chronological order of blocks.
- Nonce: This is a random number used in the mining process. Miners adjust the nonce to find a hash that meets the network's difficulty target, a process known as proof of work.
- Difficulty Target: This determines how hard it is to find a valid hash for the block. It adjusts over time to maintain a consistent block creation rate.
Block Body
The block body is where the actual blockchain transactions are stored. Each transaction is a record of an exchange between parties, such as the transfer of cryptocurrency. The transactions are bundled together and included in the block. But how are these transactions verified and secured?
Each transaction in the block body is digitally signed by the sender, ensuring its authenticity. The transactions are also linked to each other using a Merkle tree, a data structure that allows for efficient and secure verification of the transactions. This ensures that any tampering with a transaction will be immediately detectable.
The Importance of Blockchain Components
Understanding the components of a blockchain block is crucial for grasping the full potential of blockchain technology. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the security, transparency, and immutability of the blockchain.
Blockchain Security
Blockchain security is one of the most significant advantages of this technology. The use of cryptographic hashes, digital signatures, and proof of work ensures that the blockchain is tamper-proof. Any attempt to alter a block will change its hash, breaking the chain and alerting the network. This makes blockchain an ideal solution for secure transactions and data storage.
Transparency and Immutability
Transparency and immutability are two other key benefits of blockchain technology. The blockchain data structure ensures that all transactions are transparent and can be verified by anyone on the network. Once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the immutability of the data. This makes blockchain an ideal solution for applications that require high levels of trust and accountability.
Real-World Applications
So, what does all this mean for you and me? The components of a blockchain block have far-reaching implications for various industries. From finance to supply chain management, blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we conduct transactions and store data.
In the financial sector, blockchain is being used to create secure and transparent payment systems. Companies like Ripple are using blockchain to facilitate fast and low-cost international money transfers. In supply chain management, blockchain is being used to track the movement of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption, ensuring transparency and accountability.
But the applications of blockchain technology don't stop there. In healthcare, blockchain is being used to secure patient data and ensure its integrity. In voting systems, blockchain is being used to create secure and transparent voting processes. The possibilities are endless, and the future of blockchain technology looks bright.
Conclusion
So, what's inside a blockchain block? A lot more than you might think. From the block header to the block body, each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the security, transparency, and immutability of the blockchain. Understanding these components is key to unlocking the full potential of blockchain technology.
As we continue to explore the possibilities of blockchain, it's essential to stay informed and engaged. Whether you're a developer, a business owner, or simply someone interested in the future of technology, there's always more to learn and discover. So, dive in, explore, and let's build a more secure and transparent world together.
FAQs
What is the primary purpose of a blockchain block?
A blockchain block serves as a digital container that holds a set of transactions. Its primary purpose is to ensure the security, transparency, and immutability of these transactions.
How does the block header contribute to blockchain security?
The block header contains metadata that identifies the block and ensures its integrity. Components like the previous block hash and Merkle root create a tamper-proof chain, alerting the network to any attempts at alteration.
What is the role of the Merkle root in a blockchain block?
The Merkle root is a cryptographic hash that represents all the transactions in the block. It acts as a digital fingerprint, ensuring that any change in the transactions will alter the Merkle root, thus maintaining blockchain security.
How are transactions verified in a blockchain block?
Transactions in a blockchain block are digitally signed by the sender and linked using a Merkle tree. This data structure allows for efficient and secure verification, ensuring that any tampering with a transaction will be immediately detectable.
What are some real-world applications of blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology has a wide range of applications, from secure payment systems in finance to transparent supply chain management. It is also used in healthcare for securing patient data and in voting systems for creating secure and transparent voting processes.
```
Posting Komentar