
Choosing the right business structure is like selecting the foundation for your dream house. It's a decision that will impact your business's stability, growth, and long-term success. With numerous options available, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. But fear not! This guide will walk you through the process, ensuring you understand the various business entities, their legal structures, tax implications, and liability protections. So, let's dive in and find the best fit for your entrepreneurial journey.
Understanding Business Entities
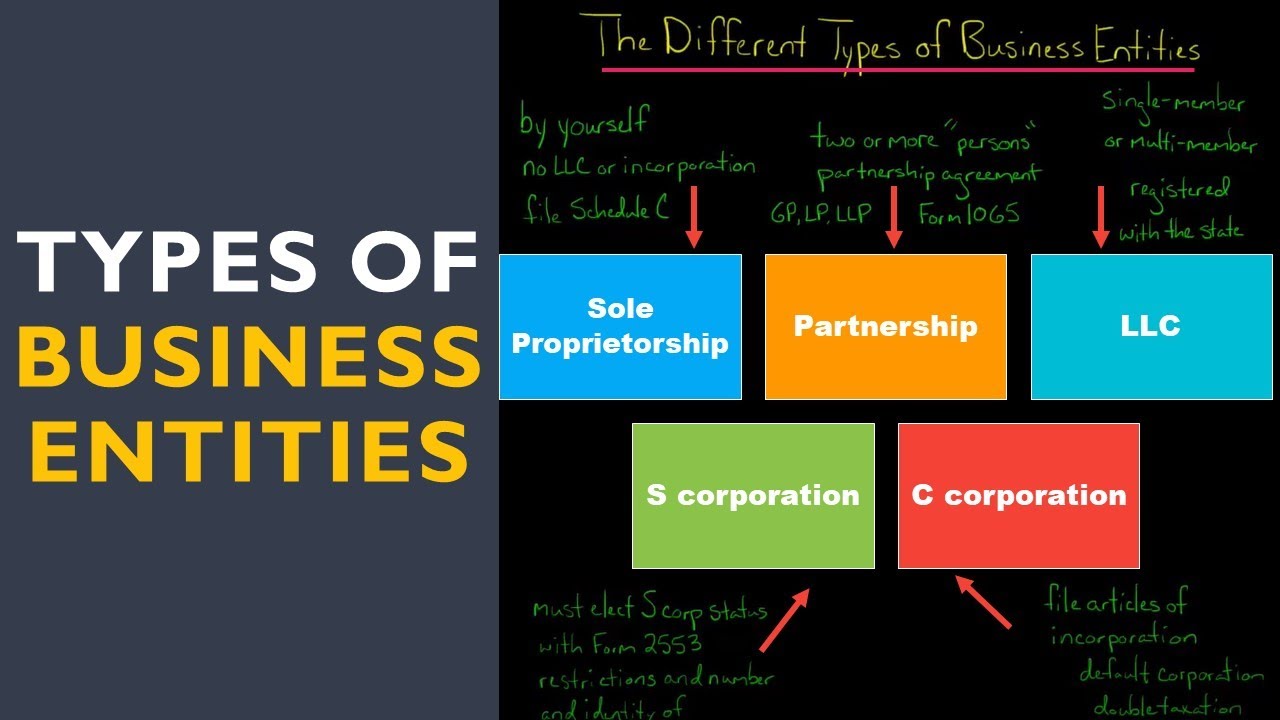
Before we delve into the details, let's understand what a business entity is. Simply put, it's the legal structure you choose for your business. Your choice will determine how your business is taxed, the level of liability protection you receive, and the complexity of formation and maintenance.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common business entity. It's like being a one-person band—you're the sole owner and operator.
- Pros: Easy to set up, minimal paperwork, and pass-through taxation.
- Cons: Unlimited personal liability, meaning your personal assets are at risk if your business faces financial trouble.
Partnership
A partnership is like a duet—two or more individuals sharing ownership and responsibilities.
- Pros: Shared financial commitment, complementary skills, and pass-through taxation.
- Cons: Joint liability, potential disagreements, and shared profits.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is a hybrid entity, combining the flexibility of a partnership with the liability protection of a corporation. Think of it as a musical group where each member has their own solo projects but comes together for performances.
- Pros: Limited liability protection, flexible management, and pass-through taxation.
- Cons: More complex to set up than a sole proprietorship or partnership, and self-employment taxes.
Corporation
A corporation is a separate legal entity, like an orchestra with a clear hierarchy and structure.
- Pros: Limited liability protection, ability to raise capital through stock, and potential tax benefits.
- Cons: Double taxation (corporate and personal), complex formation, and strict regulations.
S Corporation
An S Corporation is a special type of corporation, designed to avoid double taxation. It's like a chamber orchestra—smaller and more flexible.
- Pros: Pass-through taxation, limited liability protection, and ability to raise capital.
- Cons: Strict qualification requirements, limited stock issuance, and complex formation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Business Structure
Liability Protection
Liability protection is like a safety net. It ensures your personal assets are safe if your business faces financial trouble. LLCs and corporations offer the strongest liability protection.
Tax Implications
Tax implications are like the cost of doing business. Different business entities are taxed differently. For example, corporations face double taxation, while LLCs and S Corporations enjoy pass-through taxation.
Business Formation and Maintenance
Business formation is like setting up the stage for your performance. Some entities, like sole proprietorships, are easy to set up, while others, like corporations, require more complex paperwork.
Future Goals
Your future goals are like your encore performance. If you plan to expand, raise capital, or go public, a corporation might be the best fit. If you prefer simplicity and flexibility, an LLC might be more suitable.
How to Choose the Best Business Structure
Choosing the best business structure involves weighing the pros and cons of each entity against your business needs and future goals. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Assess Your Needs: Consider your liability protection needs, tax preferences, and future goals.
- Research: Learn about the different business entities, their legal structures, tax implications, and liability protections.
- Consult a Professional: Speak with a business attorney or accountant. They can provide personalized advice based on your unique situation.
- Make a Decision: Choose the business structure that best fits your needs.
- Form Your Business: Follow the necessary steps to form your business entity. This may involve filing paperwork with your state, obtaining an EIN, and creating an operating agreement or bylaws.
Conclusion
Choosing the best business structure is a critical decision that will impact your business's stability, growth, and long-term success. It's like selecting the foundation for your dream house—it requires careful consideration and planning. But with the right information and guidance, you can make an informed decision that sets your business up for success.
Remember, there's no one-size-fits-all answer. The best business structure depends on your unique needs, preferences, and future goals. So, take the time to assess your needs, research your options, and consult with a professional. Your business will thank you for it.
FAQs
Can I change my business structure later? Yes, you can change your business structure later. However, it may involve complex paperwork and potential tax consequences. It's best to choose the right structure from the start, but don't let fear of change prevent you from growing your business.
Which business structure offers the best tax benefits? The business structure that offers the best tax benefits depends on your unique situation. LLCs and S Corporations offer pass-through taxation, while corporations may offer tax benefits for larger businesses. Consult with a tax professional to determine the best option for you.
Do I need an attorney to form a business? While you don't necessarily need an attorney to form a business, consulting with one can be beneficial. An attorney can provide personalized advice, help you navigate complex paperwork, and ensure you're complying with all legal requirements.
What is pass-through taxation? Pass-through taxation is a tax structure where the business's income and expenses are passed through to the owners' personal tax returns. This can help avoid double taxation and may result in lower overall taxes.
How do I know if my business needs liability protection? If your business involves significant financial risk, deals with sensitive customer data, or operates in an industry with high litigation risk, you may need liability protection. Liability protection ensures your personal assets are safe if your business faces financial trouble or legal issues.

For more information on business structures, visit the U.S. Small Business Administration and IRS websites. These resources provide detailed guides and tools to help you choose the best business structure for your needs.
Posting Komentar