Embarking on a new business venture is like setting sail on an exciting journey. One of the first critical decisions you'll make is choosing the right business structure. This choice can significantly impact your startup's legal protection, tax implications, and overall success. So, how do you navigate this crucial step? Let's dive in and explore the various business entities and how to select the one that best suits your needs.
Understanding Business Structures
Before you can choose the right business structure, it's essential to understand the different types available. Each has its unique advantages and disadvantages, particularly concerning liability protection and tax implications.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common business structure. It's easy to set up and offers complete control over your business. However, it also comes with unlimited personal liability, meaning your personal assets are at risk if your business faces legal issues or debts.
Partnership
A partnership is similar to a sole proprietorship but involves two or more people. There are two main types: general partnerships and limited partnerships. In a general partnership, all partners share equal responsibility for the business. In a limited partnership, some partners have limited liability but also limited control over the business.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC combines the best of both worlds: the flexibility of a partnership and the liability protection of a corporation. LLCs are popular among small businesses because they offer personal asset protection and pass-through taxation, meaning profits and losses are reported on the owners' personal income tax returns.
Corporation
A corporation is a separate legal entity from its owners, offering the strongest liability protection. There are two main types: C corporations and S corporations. C corporations are subject to double taxation, while S corporations avoid this by passing corporate income, losses, deductions, and credits through to their shareholders.
Cooperative
A cooperative is a business owned and controlled by the people who use its services. Profits are distributed among the members, and decisions are made democratically. Cooperatives are less common but can be beneficial for certain types of businesses, such as agricultural or retail cooperatives.
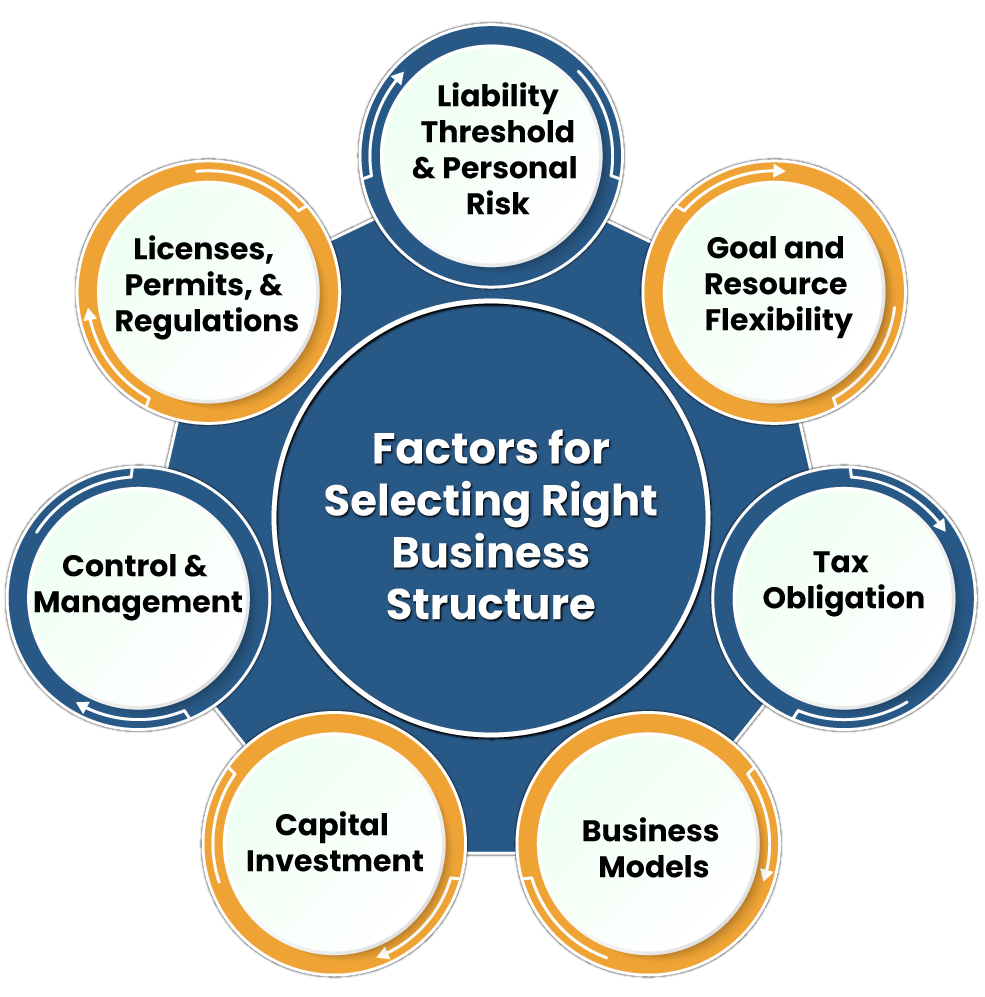
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Business Structure
Now that you understand the different types of business structures, let's explore the key factors to consider when making your choice.
Liability Protection
One of the most critical factors is liability protection. If your business faces legal issues or debts, you'll want to ensure your personal assets are protected. LLCs and corporations offer the strongest liability protection, while sole proprietorships and partnerships offer little to none.
Tax Implications
Tax implications are another crucial factor. Different business structures have different tax requirements and benefits. For example, LLCs and S corporations offer pass-through taxation, while C corporations are subject to double taxation. It's essential to consult with a tax professional to understand the tax implications of each structure.
Management and Control
Consider how much control you want over your business. Sole proprietorships and LLCs offer the most control, while corporations have a more complex management structure with a board of directors and shareholders.
Future Growth
Think about your business's future growth. If you plan to seek outside investment or go public, a corporation may be the best choice. However, if you plan to keep your business small and simple, a sole proprietorship or LLC may be more suitable.
Legal and Administrative Requirements
Different business structures have different legal and administrative requirements. For example, corporations have more complex filing and reporting requirements than sole proprietorships or LLCs. It's essential to understand these requirements and ensure you can meet them.
How to Choose the Right Business Structure for Your Company
Choosing the right business structure involves weighing the pros and cons of each type and considering your business's unique needs and goals. Here are some steps to guide you through the process:
Step 1: Assess Your Business Needs
Start by assessing your business needs. What are your short-term and long-term goals? What are your priorities regarding liability protection, tax implications, and management control?
Step 2: Research Different Business Structures
Research the different business structures available. Understand their advantages and disadvantages, particularly concerning liability protection and tax implications.
Step 3: Consult with Professionals
Consult with professionals, such as a business attorney or tax advisor. They can provide valuable insights and help you understand the legal and tax implications of each structure.
Step 4: Consider Your Future Plans
Consider your future plans. Do you plan to seek outside investment or go public? Do you plan to keep your business small and simple? Your future plans can significantly impact your choice of business structure.
Step 5: Make an Informed Decision
Based on your research and consultations, make an informed decision. Choose the business structure that best suits your business's unique needs and goals.
Conclusion
Choosing the right business structure is a critical decision that can significantly impact your startup's success. By understanding the different types of business structures and considering the key factors, you can make an informed decision that best suits your business's unique needs and goals. Remember, there's no one-size-fits-all solution. What works for one business may not work for another.
So, are you ready to set sail on your business journey? Take the time to choose the right business structure, and you'll be well on your way to success.
FAQs
1. What is the easiest business structure to set up?
The easiest business structure to set up is a sole proprietorship. It requires minimal paperwork and can be established quickly. However, it offers no liability protection, so it may not be the best choice for all businesses.
2. What is the difference between an LLC and a corporation?
An LLC combines the flexibility of a partnership with the liability protection of a corporation. It offers pass-through taxation, meaning profits and losses are reported on the owners' personal income tax returns. A corporation is a separate legal entity from its owners, offering the strongest liability protection. It has a more complex management structure and is subject to double taxation unless it elects S corporation status.
3. Can I change my business structure later?
Yes, you can change your business structure later. However, it can be a complex process involving legal and tax implications. It's essential to consult with a business attorney or tax advisor before making any changes.
4. What is the best business structure for a small business?
The best business structure for a small business depends on its unique needs and goals. Many small businesses choose LLCs because they offer liability protection and pass-through taxation. However, sole proprietorships and partnerships may also be suitable for some small businesses.
5. How do I register my business structure?
The process of registering your business structure varies depending on the type of business and your location. Generally, you'll need to file paperwork with your state's Secretary of State office and pay a filing fee. It's essential to consult with a business attorney or your state's Secretary of State office for specific instructions.

By following these steps and considering these factors, you can choose the right business structure for your company and set your startup on the path to success.
Posting Komentar