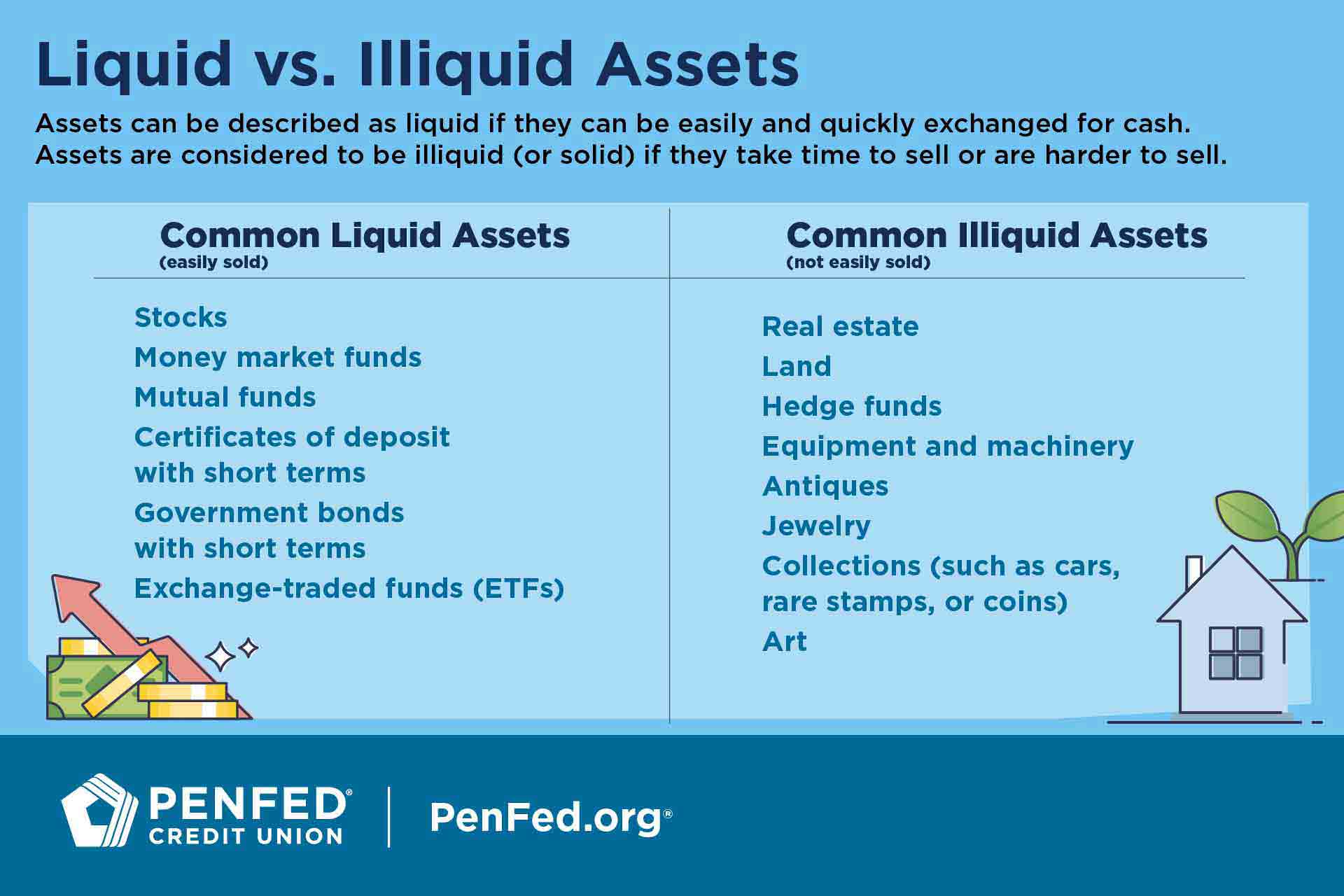
Imagine you have a treasure chest filled with gold coins. You can easily convert these coins into cash whenever you need it, right? Now, think of stocks as another form of treasure. But are they as easily convertible into cash? This is the question we'll explore in this article. Understanding whether stocks are considered liquid assets is crucial for your financial planning and investment strategies. So, let's dive in and unravel the mystery behind the liquidity of stocks.
Understanding Liquidity in the Stock Market
Liquidity refers to how quickly and easily an asset can be converted into cash without affecting its market value. In the context of the stock market, liquidity is about how swiftly you can buy or sell stocks without causing significant price fluctuations. High liquidity means you can enter or exit a position with minimal impact on the stock's price. But does this make stocks liquid assets?
What Makes a Stock Liquid?
Several factors determine the liquidity of a stock. These include:
- Trading Volume: The number of shares traded in a given period. High trading volume indicates high liquidity.
- Market Depth: The number of buy and sell orders at various price levels. Deep markets have more orders, making it easier to execute large trades without affecting the price.
- Bid-Ask Spread: The difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. A narrow spread indicates high liquidity.
For example, stocks like Apple (AAPL) or Microsoft (MSFT) are highly liquid because they have high trading volumes and deep markets. On the other hand, smaller, less-known companies may have lower liquidity, making it harder to buy or sell their stocks quickly.
The Role of Market Volatility
Market volatility can significantly impact the liquidity of stocks. During periods of high market volatility, such as during economic crises or major geopolitical events, the stock market can become less liquid. Investors may be more cautious, leading to fewer trades and wider bid-ask spreads. This makes it harder to convert stocks into cash quickly, affecting their liquidity.
Think of market volatility as a stormy sea. When the waters are calm, it's easy to navigate and trade stocks. But when the storm hits, the sea becomes choppy, making it difficult to move around. Similarly, high market volatility can make the stock market turbulent, reducing liquidity.
Stocks vs. Other Liquid Assets
Compared to other liquid assets like cash or government bonds, stocks generally have lower liquidity. Cash is the most liquid asset because it can be used immediately for transactions. Government bonds are also highly liquid, especially those issued by stable governments. But what about stocks?
Stocks can be liquid, but their liquidity varies greatly. Blue-chip stocks from large, established companies tend to be more liquid. These stocks are traded frequently and have deep markets, making them easier to convert into cash. However, stocks from smaller companies or those in niche markets may have lower liquidity, making them less suitable for quick conversions.
So, are stocks considered liquid assets? The answer is nuanced. While some stocks can be highly liquid, others may not be. It depends on the specific stock and the current market conditions.
The Importance of Liquidity in Financial Planning
Understanding the liquidity of stocks is essential for effective financial planning. If you need quick access to cash, investing in highly liquid stocks can be beneficial. However, if you're planning for long-term growth, you might be more willing to accept lower liquidity in exchange for higher potential returns.
For instance, if you're saving for a down payment on a house, you might prefer to invest in highly liquid assets like money market funds or short-term government bonds. But if you're investing for retirement, you might include a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets in your portfolio, balancing liquidity with growth potential.
Strategies for Managing Stock Liquidity
Here are some strategies to manage the liquidity of your stock investments:
Diversify Your Portfolio
Diversification is key to managing liquidity. By spreading your investments across different types of stocks and other assets, you can balance liquidity and risk. Include a mix of highly liquid blue-chip stocks and less liquid but potentially high-growth stocks in your portfolio.
Monitor Market Conditions
Stay informed about market conditions and adjust your investment strategy accordingly. During periods of high market volatility, you might want to hold more liquid assets. Conversely, during stable market conditions, you can consider investing in less liquid stocks for potential higher returns.
Use Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders can help manage the liquidity of your stock investments. By setting a stop-loss order, you can automatically sell a stock if its price falls to a certain level, ensuring you can convert it into cash quickly if needed.
Conclusion
So, are stocks considered liquid assets? The answer is yes, but with a caveat. Some stocks are highly liquid, making them easy to convert into cash quickly. Others may have lower liquidity, depending on the specific stock and market conditions. Understanding the liquidity of stocks is crucial for your financial planning and investment strategies. By diversifying your portfolio, monitoring market conditions, and using tools like stop-loss orders, you can effectively manage the liquidity of your stock investments.
Now, it's your turn to take action. Review your investment portfolio and assess the liquidity of your stocks. Consider diversifying your investments and staying informed about market conditions. By doing so, you can make informed decisions and achieve your financial goals.
FAQs
1. What are some examples of highly liquid stocks?
Highly liquid stocks typically include those of large, well-established companies with high trading volumes and deep markets. Examples include Apple (AAPL), Microsoft (MSFT), and Amazon (AMZN).
2. How does market volatility affect stock liquidity?
During periods of high market volatility, the stock market can become less liquid. Investors may be more cautious, leading to fewer trades and wider bid-ask spreads, making it harder to convert stocks into cash quickly.
3. Why is understanding stock liquidity important for financial planning?
Understanding stock liquidity is crucial for effective financial planning because it helps you manage your investments based on your cash needs and risk tolerance. Highly liquid stocks can provide quick access to cash, while less liquid stocks may offer higher potential returns for long-term growth.
4. What strategies can I use to manage the liquidity of my stock investments?
Strategies for managing stock liquidity include diversifying your portfolio, monitoring market conditions, and using tools like stop-loss orders. Diversification helps balance liquidity and risk, while staying informed about market conditions allows you to adjust your investment strategy accordingly.
5. Are there any risks associated with investing in highly liquid stocks?
While highly liquid stocks offer the advantage of quick conversion to cash, they may also be more volatile and subject to market fluctuations. Additionally, the focus on liquidity might lead to lower potential returns compared to less liquid but high-growth stocks.
```
Posting Komentar