Imagine walking into a bustling marketplace where buyers and sellers are constantly haggling over prices. Now, picture a savvy trader who ensures that there's always a buyer for every seller and a seller for every buyer. This trader is the lifeblood of the market, ensuring liquidity and stability. Welcome to the world of market makers, the unsung heroes of financial markets. But how do market makers make money? Let's dive in and explore the intriguing world of market maker strategies and revenue models.
Understanding Market Makers
Market makers are financial institutions or individuals who provide liquidity to financial markets by continuously buying and selling securities. They act as intermediaries, ensuring that there is always a market for traders to buy or sell assets. But how do these market makers generate profits in such a competitive and dynamic environment?
The Role of Market Makers in Financial Markets
In the vast landscape of financial markets, market makers play a crucial role. They facilitate trading by providing quotes for both buying and selling prices, thereby narrowing the bid-ask spread. This process not only enhances market efficiency but also attracts more traders, increasing overall market activity. Think of market makers as the glue that holds the market together, ensuring smooth operations and reducing volatility.
Market Maker Strategies
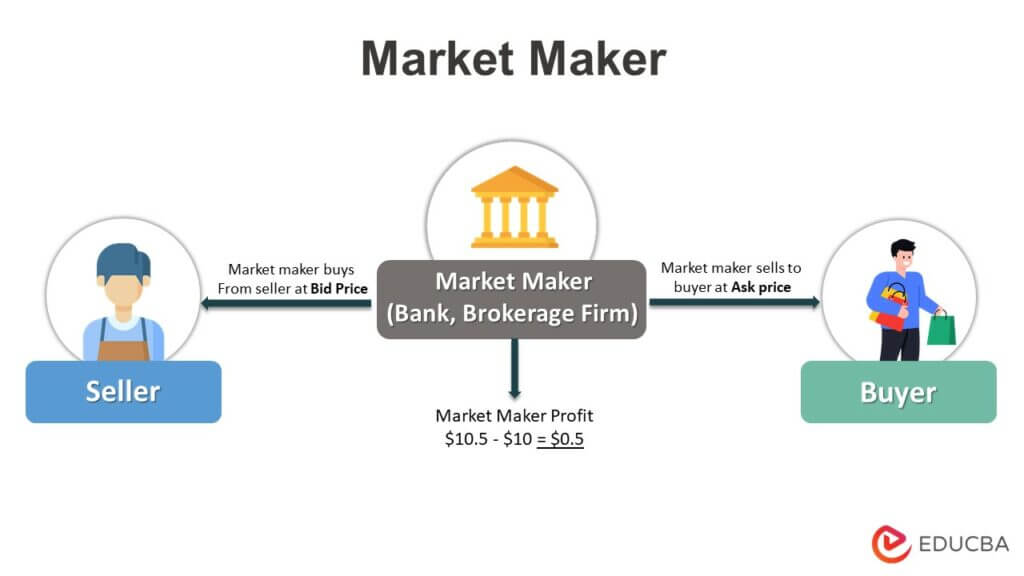
So, how do market makers make money? The answer lies in their sophisticated market maker strategies. These strategies are designed to capitalize on the bid-ask spread, the difference between the buying and selling prices of a security. By continuously quoting prices and executing trades, market makers can generate trading profits. But how do they manage to do this without taking on too much risk?
One of the primary strategies employed by market makers is arbitrage. Arbitrage involves exploiting price differences between different markets or exchanges. For example, if a stock is trading at a higher price on one exchange and a lower price on another, a market maker can buy the stock at the lower price and sell it at the higher price, pocketing the difference as profit. This strategy requires quick decision-making and advanced technology to execute trades in real-time.
Another key strategy is inventory management. Market makers need to maintain a balanced inventory of securities to avoid significant price movements that could impact their profits. By carefully managing their inventory, market makers can minimize risk and maximize profits. This involves constantly monitoring market conditions and adjusting their positions accordingly.
Revenue Models of Market Makers
Now that we understand the strategies, let's delve into the revenue models that market makers use to generate profits. The primary revenue model for market makers is the bid-ask spread. By setting a narrow spread, market makers can attract more traders, increasing their trading volume and, consequently, their profits. But how do they ensure that the spread is narrow enough to attract traders without compromising their profits?
Market makers also generate revenue through commissions and fees. In some cases, they may charge traders a small fee for executing trades. Additionally, market makers can earn interest on the capital they use to maintain their inventory of securities. This interest income can be a significant source of revenue, especially in low-volatility markets.
Moreover, market makers can engage in proprietary trading, where they use their own capital to execute trades based on their market insights and analysis. This can be a high-risk, high-reward strategy, but when executed correctly, it can generate substantial profits.
Market Operations and Risk Management
To sustain their profitability, market makers must excel in market operations and risk management. Market operations involve the day-to-day activities of providing liquidity, executing trades, and managing inventory. Effective market operations require advanced technology, real-time data analysis, and quick decision-making.
Risk management is equally crucial. Market makers face various risks, including market risk, credit risk, and operational risk. To mitigate these risks, market makers employ sophisticated risk management techniques, such as hedging, diversification, and stress testing. By carefully managing their risks, market makers can ensure the sustainability of their trading profits.
Conclusion
In the dynamic world of financial markets, market makers play a pivotal role in ensuring liquidity and stability. Through their sophisticated market maker strategies and revenue models, they generate trading profits while managing risks effectively. From arbitrage to inventory management, from the bid-ask spread to proprietary trading, market makers employ a variety of techniques to stay ahead in the game. So, the next time you execute a trade, remember the unsung heroes behind the scenes, the market makers, who make it all possible.
Now, I'd love to hear your thoughts. Have you ever considered the role of market makers in financial markets? What strategies do you think are most effective for generating profits? Share your insights in the comments below!
FAQs
1. What is the primary role of a market maker?
A market maker's primary role is to provide liquidity to financial markets by continuously buying and selling securities. They ensure that there is always a market for traders to buy or sell assets, thereby enhancing market efficiency and stability.
2. How do market makers generate profits?
Market makers generate profits through various strategies, including arbitrage, inventory management, and proprietary trading. Their primary revenue model is the bid-ask spread, where they profit from the difference between the buying and selling prices of a security.
3. What are some common market maker strategies?
Common market maker strategies include arbitrage, where they exploit price differences between different markets or exchanges, and inventory management, where they maintain a balanced inventory of securities to minimize risk and maximize profits.
4. How do market makers manage risks?
Market makers manage risks through sophisticated techniques such as hedging, diversification, and stress testing. These techniques help them mitigate market risk, credit risk, and operational risk, ensuring the sustainability of their trading profits.
5. What is the bid-ask spread, and how does it relate to market makers?
The bid-ask spread is the difference between the buying and selling prices of a security. Market makers profit from this spread by setting narrow spreads that attract more traders, increasing their trading volume and, consequently, their profits.
```
Posting Komentar