Imagine you're at a bustling marketplace, and you want to know the total worth of a particular stall. You'd look at how many items they have and how much each item is worth, right? In the world of finance, determining the total worth of a company is similarly straightforward, yet incredibly powerful. This metric is known as market capitalization, or market cap for short. Understanding how market cap is calculated is crucial for anyone involved in investment analysis and stock valuation. So, let's dive in and demystify this essential financial metric.
The Basics of Market Capitalization
Market capitalization is essentially the total equity value of a company. It's calculated by multiplying the current share price by the total number of outstanding shares. Think of it as the financial equivalent of measuring the size of a company. Just as you wouldn't compare a small boutique to a massive retail chain, you wouldn't evaluate a small-cap stock the same way you would a blue-chip giant.
Why Does Market Cap Matter?
Market cap is more than just a number; it's a key indicator of a company's size and stability. Investors use it to gauge the risk and potential returns of a stock. For instance, large-cap stocks are often seen as safer bets because they are usually well-established companies with a proven track record. On the other hand, small-cap stocks can offer higher growth potential but come with greater risk.
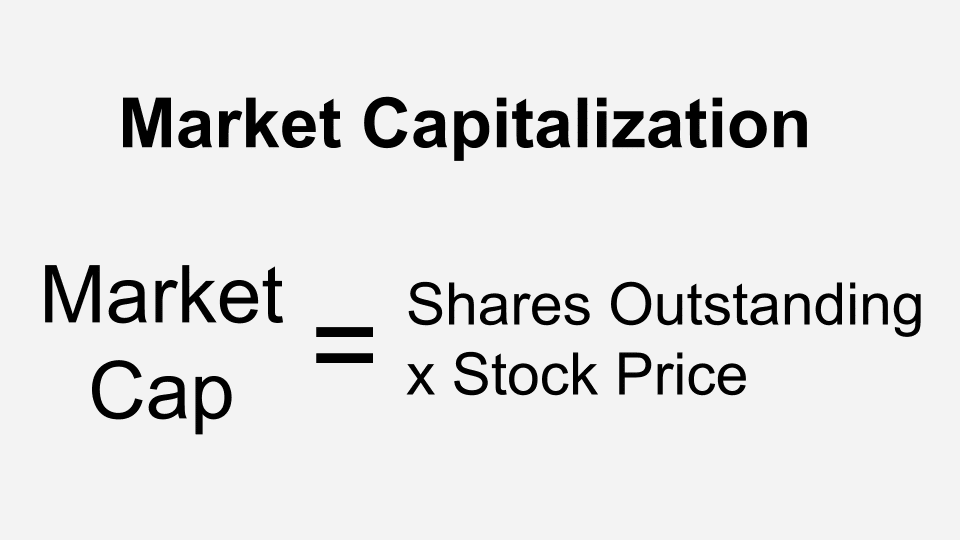
How Is Market Cap Calculated?
Calculating market cap is surprisingly simple. You need two pieces of information: the current share price and the total number of outstanding shares. The formula is straightforward:
Market Cap = Current Share Price × Total Number of Outstanding Shares
Let's break it down with an example. Suppose Company XYZ has 1 million shares outstanding, and each share is currently trading at $50. To find the market cap, you would multiply 1 million by $50, resulting in a market cap of $50 million.
Understanding Outstanding Shares
Outstanding shares refer to all the shares that are currently owned by investors, including restricted shares owned by insiders and institutional investors. These shares are actively traded on the stock market and contribute to the company's market cap. It's important to note that this excludes treasury shares, which are shares that the company has repurchased and holds in its treasury.
The Role of Share Price
The share price is the current market value of a single share of stock. It fluctuates based on supply and demand, economic conditions, and company performance. When the share price increases, the market cap also increases, assuming the number of outstanding shares remains constant. Conversely, a decrease in share price will lower the market cap.
Market Cap Categories
Companies are often categorized based on their market cap. These categories help investors understand the relative size and risk profile of a company. Here are the main categories:
Large-Cap Stocks
Large-cap stocks, also known as blue-chip stocks, typically have a market cap of $10 billion or more. These companies are usually well-established and have a history of stable earnings. Examples include tech giants like Apple and Microsoft. Investing in large-cap stocks is often seen as less risky because these companies have the resources to weather economic storms.
Mid-Cap Stocks
Mid-cap stocks have a market cap between $2 billion and $10 billion. These companies are often in a growth phase and can offer a good balance between risk and reward. They may have the potential for significant growth but come with more volatility than large-cap stocks.
Small-Cap Stocks
Small-cap stocks have a market cap between $300 million and $2 billion. These companies are often in the early stages of development and can offer high growth potential. However, they also come with higher risk due to their smaller size and limited resources.
Micro-Cap and Nano-Cap Stocks
Micro-cap stocks have a market cap between $50 million and $300 million, while nano-cap stocks have a market cap below $50 million. These companies are typically very small and can be highly volatile. Investing in micro-cap and nano-cap stocks requires a higher risk tolerance and a deeper understanding of the company's fundamentals.
Market Cap vs. Other Financial Metrics
While market cap is a crucial metric, it's not the only one you should consider when evaluating a company. Other financial metrics like earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings ratio (P/E ratio), and debt-to-equity ratio can provide a more comprehensive view of a company's health and potential. For example, a high P/E ratio might indicate that a stock is overvalued, while a low debt-to-equity ratio suggests financial stability.
For a deeper dive into these metrics, you might want to explore resources like Investopedia's guide to EPS or CFI's explanation of the P/E ratio.
Conclusion
Understanding how market cap is calculated is a fundamental skill for any investor. It provides a snapshot of a company's size and market value, helping you make informed decisions. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting out, knowing how to calculate and interpret market cap can significantly enhance your investment analysis. So, the next time you're evaluating a stock, remember to consider its market cap alongside other key financial metrics.
Now that you're equipped with this knowledge, why not put it into practice? Start by looking up the market cap of your favorite companies and see how it compares to their peers. The more you practice, the more confident you'll become in your investment decisions.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between market cap and enterprise value?
Market cap focuses solely on the equity value of a company, while enterprise value includes both equity and debt. Enterprise value provides a more comprehensive view of a company's total value, including its debt obligations.
2. Can market cap change daily?
Yes, market cap can change daily as the share price fluctuates. Since the share price is a key component of the market cap calculation, any changes in the share price will directly affect the market cap.
3. Why is market cap important for investors?
Market cap is important because it helps investors understand the size and risk profile of a company. It's a key metric for comparing companies within the same industry and for making informed investment decisions.
4. How do I find the market cap of a company?
You can find the market cap of a company on financial websites like Yahoo Finance, Google Finance, or the company's investor relations page. These platforms provide up-to-date information on share prices and outstanding shares, allowing you to calculate the market cap.
5. What are the limitations of using market cap for investment analysis?
While market cap is a useful metric, it has its limitations. It doesn't provide insight into a company's profitability, debt levels, or future growth prospects. Therefore, it's important to use market cap in conjunction with other financial metrics for a more comprehensive analysis.
```
Posting Komentar