How Does Cryptography Secure Blockchain?
Imagine a world where your digital transactions are as secure as a fortress, where your data is protected by an impenetrable shield, and where trust is not just a word but a guarantee. Welcome to the world of blockchain, where cryptography behind blockchain is the unsung hero making all this possible. But how exactly does cryptography secure blockchain? Let's dive in and explore the fascinating intersection of cryptography and blockchain technology.
The Foundation of Blockchain Security
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. But what makes these transactions secure? The answer lies in the sophisticated use of cryptographic algorithms and cryptographic protocols that ensure data integrity and secure transactions. Think of cryptography as the lock and key system that protects your digital assets. Without it, blockchain would be vulnerable to hackers and fraudsters.
Understanding Cryptographic Algorithms
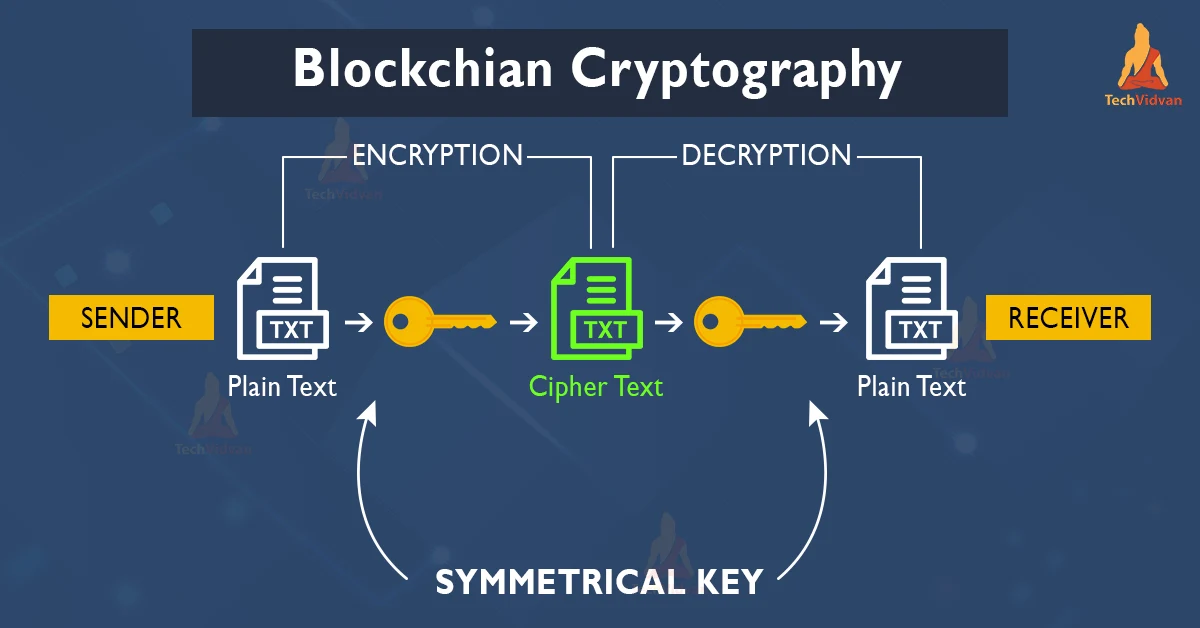
Cryptographic algorithms are the mathematical formulas that transform readable data into an unreadable format. This process, known as encryption, is crucial for securing transactions on the blockchain. When you initiate a transaction, the data is encrypted using a public key, which is a unique identifier. Only the corresponding private key can decrypt this data, ensuring that only the intended recipient can access it. This dual-key system is the backbone of blockchain encryption.
One of the most commonly used cryptographic algorithms in blockchain is the SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit). This algorithm takes an input (or 'message') and returns a fixed-size string of characters, which is virtually impossible to reverse-engineer. This ensures that even if someone intercepts the data, they won't be able to decipher it without the private key.
The Role of Cryptographic Protocols
Cryptographic protocols are the rules and procedures that govern how cryptographic algorithms are used. In the context of blockchain, these protocols ensure that transactions are verified and validated in a secure manner. For example, the Proof of Work (PoW) protocol requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to add new blocks to the chain. This process not only validates transactions but also makes it extremely difficult for anyone to tamper with the data.
Another important protocol is the Proof of Stake (PoS), which relies on validators who stake their own cryptocurrency to verify transactions. This protocol is more energy-efficient than PoW and still ensures a high level of security. Both protocols use cryptographic techniques to maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
Ensuring Data Integrity
Data integrity is the assurance that data has not been altered in an unauthorized manner. In blockchain, data integrity is maintained through the use of hashes. Each block in the blockchain contains a unique hash that is generated from the data within the block. If any data within the block is changed, the hash will also change, alerting the network to potential tampering.
This hash-based system creates a chain of blocks, where each block is linked to the previous one. Any attempt to alter a block would require changing all subsequent blocks, making it practically impossible to tamper with the data without detection. This is why blockchain is often referred to as an immutable ledger.
The Importance of Secure Transactions
Secure transactions are the lifeblood of any blockchain network. Without cryptography, transactions would be vulnerable to fraud and manipulation. Cryptography ensures that only authorized parties can access and modify transaction data, providing a high level of security and trust.
For instance, when you send cryptocurrency to someone, the transaction is encrypted and broadcast to the network. Miners or validators then verify the transaction using cryptographic protocols. Once verified, the transaction is added to a block and linked to the blockchain, making it permanent and tamper-proof. This process ensures that your transaction is secure and cannot be reversed or altered.
Real-World Applications and Future Prospects
The use of cryptography in blockchain has far-reaching implications beyond just securing transactions. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management are exploring blockchain technology to enhance security and efficiency. For example, in finance, blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent financial systems, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing trust.
In healthcare, blockchain can be used to securely store and share patient data, ensuring that only authorized parties can access sensitive information. In supply chain management, blockchain can be used to track the movement of goods, ensuring transparency and reducing the risk of counterfeiting.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, so too will the role of cryptography. New cryptographic algorithms and protocols are being developed to address emerging challenges and enhance security. For instance, quantum-resistant cryptography is being explored to protect against the potential threats posed by quantum computers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cryptography behind blockchain is the invisible shield that protects your digital transactions and ensures data integrity. From cryptographic algorithms to protocols, every aspect of blockchain security relies on the principles of cryptography. As we continue to explore the potential of blockchain technology, understanding the role of cryptography will be crucial. So, the next time you make a transaction on the blockchain, remember that it's cryptography that's keeping your data secure.
Now, I'd love to hear your thoughts. How do you think cryptography will evolve in the future of blockchain technology? Share your insights in the comments below!
FAQs
1. What is the primary role of cryptography in blockchain?
The primary role of cryptography in blockchain is to ensure secure transactions and data integrity. It uses algorithms and protocols to encrypt data, making it inaccessible to unauthorized parties and preventing tampering.
2. How does blockchain encryption work?
Blockchain encryption works by transforming readable data into an unreadable format using cryptographic algorithms. This encrypted data can only be decrypted by the intended recipient using a private key, ensuring that transactions are secure and private.
3. What are some common cryptographic algorithms used in blockchain?
Some common cryptographic algorithms used in blockchain include SHA-256, which is used for hashing, and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), which is used for encryption and digital signatures. These algorithms ensure that data is secure and tamper-proof.
4. How do cryptographic protocols enhance blockchain security?
Cryptographic protocols like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) enhance blockchain security by validating transactions in a secure manner. These protocols use cryptographic techniques to ensure that only authorized transactions are added to the blockchain, preventing fraud and manipulation.
5. What is the future of cryptography in blockchain technology?
The future of cryptography in blockchain technology is promising, with new algorithms and protocols being developed to address emerging challenges. For instance, quantum-resistant cryptography is being explored to protect against the potential threats posed by quantum computers, ensuring that blockchain remains secure in the face of evolving threats.
```
Belum ada Komentar untuk " How Does Cryptography Secure Blockchain?"
Posting Komentar