Imagine you own a pie, and you decide to cut it into smaller slices. The pie itself hasn't changed in size, but now there are more pieces to go around. This is a simple analogy for what happens when stock splits occur. In the stock market, a stock split is a corporate action where a company divides its existing shares into multiple shares. But what does this mean for you as an investor? Let's dive in and explore the intricacies of stock splits, their impact on shareholder equity, and how they fit into your investment strategies.
Understanding Stock Splits
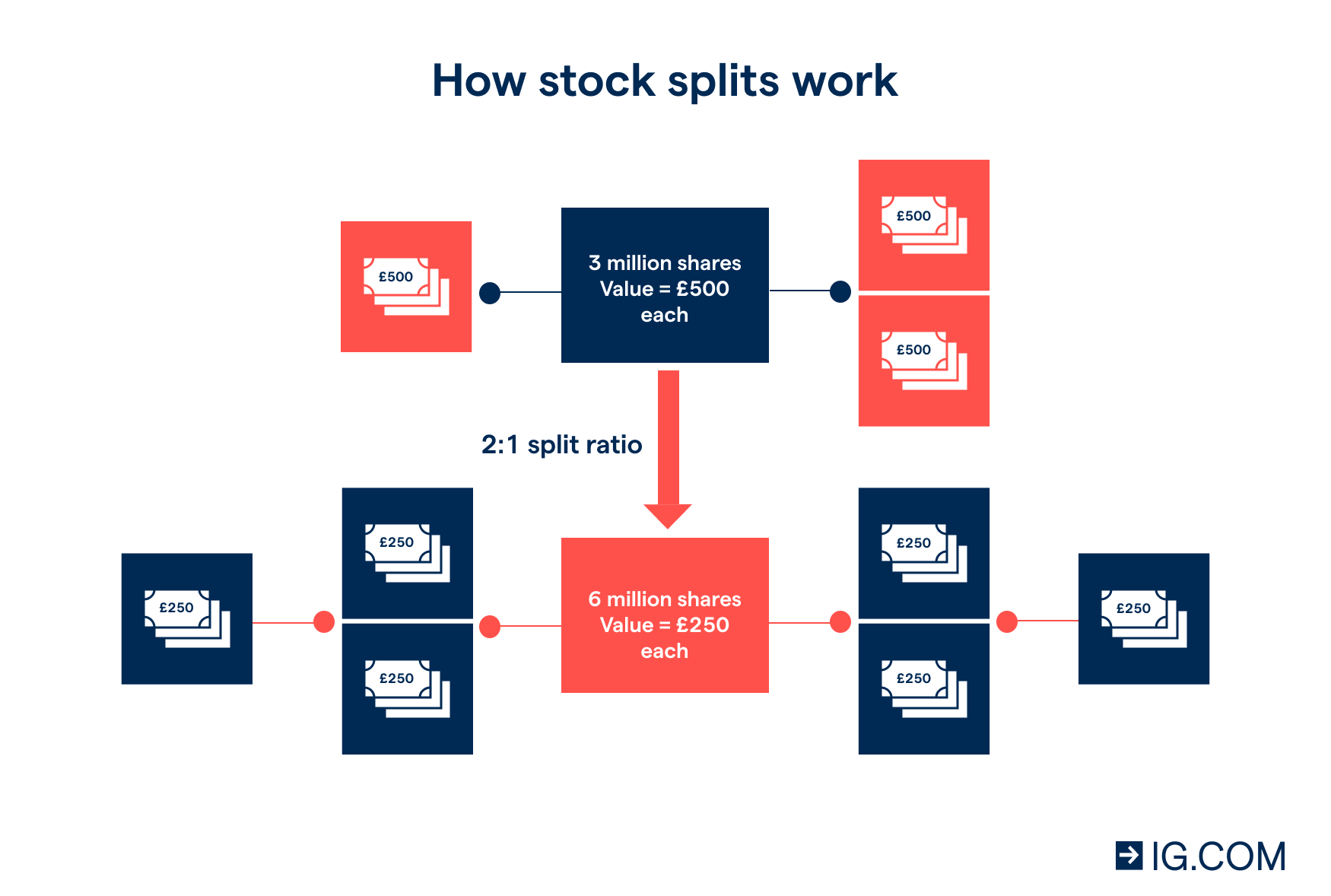
When a company announces a stock split, it's often a sign of confidence in its future growth. But what exactly is a stock split? Essentially, it's a way for a company to adjust its stock valuation without changing its market capitalization. For example, if a company with a stock price of $100 decides to split its stock 2-for-1, each shareholder will receive two shares for every one they own, and the stock price will adjust to $50 per share. The total value of the shares remains the same, but the number of shares increases.
The Mechanics of a Stock Split
Let's break down the mechanics of a stock split. Suppose you own 10 shares of a company trading at $200 per share. If the company announces a 2-for-1 stock split, you will now own 20 shares, but each share will be worth $100. The total value of your investment remains $2,000, but the number of shares has doubled. This process doesn't change your shareholder equity; it simply makes the stock more accessible to a broader range of investors.
The Impact on Shareholder Equity and Market Capitalization
One of the most common misconceptions about stock splits is that they increase shareholder equity. In reality, a stock split does not change the overall value of a company's shares. The market capitalization, which is the total value of all outstanding shares, remains unchanged. For instance, if a company has 1 million shares trading at $100 each, its market capitalization is $100 million. After a 2-for-1 split, there will be 2 million shares trading at $50 each, but the market capitalization will still be $100 million.
Stock Splits and Dividend Yield
Another important consideration is how stock splits affect dividend yield. Dividend yield is calculated as the annual dividends per share divided by the price per share. When a stock splits, the dividend per share is also adjusted proportionally. For example, if a company pays a $2 dividend on a $100 stock, the yield is 2%. After a 2-for-1 split, the stock price becomes $50, and the dividend per share becomes $1, but the yield remains 2%. So, stock splits do not affect the dividend yield, but they can make dividends more accessible to smaller investors.
Investor Behavior and Stock Performance
Stock splits often spark a lot of investor interest and can influence stock performance in the short term. Why? Because a lower stock price can make the stock more attractive to a wider range of investors. This increased demand can drive up the stock price, at least temporarily. However, it's essential to remember that the fundamental value of the company hasn't changed. The stock split is more about perception and accessibility than actual value.
Strategic Considerations for Investors
As an investor, understanding what happens when stock splits occur can help you make more informed decisions. If you're focused on long-term investment strategies, a stock split shouldn't significantly alter your financial planning. The key is to look at the underlying fundamentals of the company, such as earnings growth, revenue, and market position. A stock split is just one piece of the puzzle, and it shouldn't be the sole factor in your investment decisions.
For those engaged in more active trading, stock splits can present opportunities. The increased liquidity and potential for short-term price movements can be advantageous. However, it's crucial to have a solid understanding of the company and the market conditions before making any moves. Always remember that past performance is not indicative of future results, and thorough research is essential.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of stock splits, let's look at a few real-world examples. Apple Inc. (AAPL) has undergone several stock splits over the years. In 2020, Apple executed a 4-for-1 stock split, making its shares more accessible to retail investors. The split didn't change the company's market capitalization or shareholder equity, but it did make the stock more attractive to a broader range of investors, potentially driving up demand and stock performance in the short term.
Another example is Tesla Inc. (TSLA), which also underwent a 5-for-1 stock split in 2020. The split made Tesla's shares more affordable, leading to increased trading volume and liquidity. However, the long-term impact on stock performance was more about the company's fundamentals and market conditions than the split itself.
Conclusion
So, what happens when stock splits occur? In essence, a stock split is a corporate action that adjusts the number of shares and their price without changing the overall value of the company. It can make stocks more accessible to a broader range of investors and potentially drive short-term price movements. However, the fundamental value of the company remains the same, and long-term investors should focus on the underlying fundamentals rather than the split itself.
As you navigate the stock market, remember that stock splits are just one of many factors to consider in your investment strategies. Whether you're a long-term investor or an active trader, understanding what happens when stock splits occur can help you make more informed decisions. So, stay informed, do your research, and always keep an eye on the bigger picture.
FAQs
1. Do stock splits increase the value of my investment?
No, stock splits do not increase the value of your investment. The total value of your shares remains the same; it's just divided into more shares.
2. How do stock splits affect dividend payments?
Dividend payments are adjusted proportionally with the stock split. For example, if a company pays a $2 dividend on a $100 stock and splits 2-for-1, the dividend per share becomes $1, but the yield remains the same.
3. Should I buy a stock before or after a split?
The timing of a stock split shouldn't be the sole factor in your decision. Focus on the company's fundamentals, such as earnings growth and market position, rather than the split itself.
4. Do stock splits always lead to a rise in stock price?
Stock splits can lead to short-term price movements due to increased demand, but the long-term impact depends on the company's fundamentals and market conditions.
5. What is the difference between a stock split and a reverse stock split?
A stock split increases the number of shares and lowers the price per share, while a reverse stock split decreases the number of shares and increases the price per share. Both actions adjust the stock valuation without changing the company's market capitalization.
```
Posting Komentar