What Are Market Indicators? Your Guide
Imagine you're navigating a vast ocean. You need a compass to guide you, right? In the world of finance, market indicators are your compass. They help you navigate the complex waters of financial markets, providing crucial insights into stock market trends and economic data. But what exactly are market indicators, and how can they aid in your financial analysis and investment decisions?
Understanding Market Indicators
Market indicators are tools used to measure and analyze the performance of financial markets. They provide a snapshot of the current economic health and future prospects. Think of them as the vital signs of the economy. Just as a doctor checks your pulse and blood pressure to understand your health, investors use market indicators to gauge the health of the economy and make informed investment strategies.
Types of Market Indicators
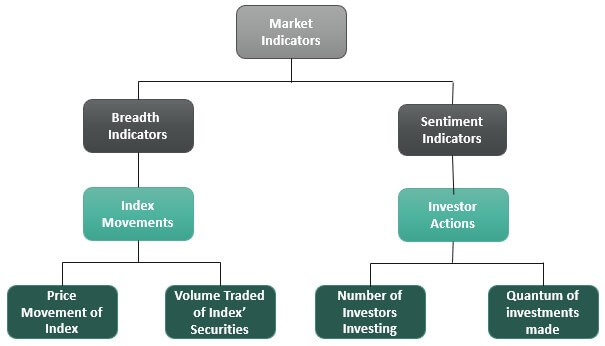
There are several types of market indicators, each serving a unique purpose. Let's dive into the main categories:
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators are metrics that provide insights into the overall health of the economy. They include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country. It's like the report card of a nation's economy.
- Unemployment Rate: Indicates the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. High unemployment can signal economic distress.
- Inflation Rate: Measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising. It's a key factor in determining the purchasing power of consumers.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): Tracks the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services.
For a deeper dive into economic indicators, you can explore resources like the Investopedia guide on economic indicators.
Financial Metrics
Financial metrics are specific measurements used to evaluate the financial health of a company. They include:
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): Indicates how much profit a company makes for each outstanding share of its common stock. It's a key metric for evaluating a company's profitability.
- Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio): Compares a company's stock price with its earnings per share. A high P/E ratio might indicate that the stock is overvalued.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Measures a company's financial leverage, calculated by dividing its total liabilities by stockholders' equity. It's a crucial metric for assessing a company's financial risk.
To learn more about financial metrics, check out the Corporate Finance Institute's guide on financial metrics.
Market Performance Indicators
These indicators focus on the performance of specific markets or sectors. They include:
- Stock Market Indices: Such as the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), and NASDAQ. These indices track the performance of a group of stocks and provide a snapshot of market trends.
- Volatility Index (VIX): Often referred to as the "fear gauge," it measures the market's expectation of volatility over the next 30 days.
- Sector Performance: Indicators that track the performance of specific sectors like technology, healthcare, or energy. These can help investors identify which sectors are outperforming or underperforming.
For more on market performance indicators, visit the Investopedia guide on market indices.
How to Use Market Indicators for Investment Decisions
So, how do you use these indicators to make better investment decisions? It's like being a detective, piecing together clues to solve a mystery. Here’s how you can do it:
Analyzing Economic Indicators
Start by looking at the big picture. Economic indicators like GDP and unemployment rates give you a sense of the overall economic health. For example, if the GDP is growing and unemployment is low, it might be a good time to invest in the stock market. Conversely, if the economy is slowing down, you might want to be more cautious.
Evaluating Financial Metrics
Next, zoom in on specific companies. Financial metrics like EPS and P/E ratio help you evaluate the financial health of individual companies. A company with a high EPS and a reasonable P/E ratio might be a good investment. But remember, no single metric tells the whole story. Always look at multiple indicators.
Monitoring Market Performance
Finally, keep an eye on market performance indicators. If the tech sector is booming, it might be a good time to invest in tech stocks. But if the VIX is high, indicating high volatility, you might want to be more conservative.
The Role of Market Indicators in Financial Analysis
Market indicators play a crucial role in financial analysis. They help you understand the past, present, and future of the market. By analyzing these indicators, you can identify trends, spot opportunities, and mitigate risks. It's like having a crystal ball, but with data-driven insights.
For instance, if you notice that the unemployment rate is dropping and consumer spending is increasing, you might predict that the economy is on an upward trajectory. This information can guide your investment strategies, helping you make more informed decisions.
Conclusion
Market indicators are your compass in the world of finance. They provide valuable insights into stock market trends and economic data, helping you make better investment decisions. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding and using market indicators can significantly improve your financial analysis and investment strategies.
So, are you ready to navigate the financial markets with confidence? Start by familiarizing yourself with the key market indicators and use them to guide your investment journey. Remember, the more you know, the better equipped you'll be to make smart investment decisions.
FAQs
1. What are the most important market indicators for beginners?
For beginners, it's essential to start with broad economic indicators like GDP, unemployment rate, and inflation rate. These give a general sense of the economic health. Additionally, familiarize yourself with stock market indices like the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average.
2. How often should I check market indicators?
The frequency depends on your investment strategy. Short-term traders might check daily, while long-term investors might review indicators monthly or quarterly. Consistency is key, so choose a frequency that aligns with your goals and stick to it.
3. Can market indicators predict future market performance?
Market indicators provide insights based on historical data and current trends, but they are not foolproof predictors. They can help you make educated guesses, but always remember that markets are influenced by a multitude of factors, including unexpected events.
4. What is the difference between leading and lagging indicators?
Leading indicators predict future economic trends, such as consumer confidence and manufacturing orders. Lagging indicators, like GDP and unemployment rate, confirm trends that have already occurred. Both are essential for a comprehensive financial analysis.
5. How do I use market indicators to diversify my portfolio?
By analyzing market indicators, you can identify sectors or asset classes that are performing well or have growth potential. Diversifying your portfolio across these areas can help mitigate risks and maximize returns. For example, if tech stocks are booming, you might allocate a portion of your portfolio to tech ETFs.
```
Belum ada Komentar untuk " What Are Market Indicators? Your Guide"
Posting Komentar